Intermodal Freight Transportation Market Size 2025-2029
The intermodal freight transportation market size is forecast to increase by USD 69.4 billion, at a CAGR of 7.2% between 2024 and 2029.
- Intermodal freight transportation is experiencing significant growth due to the reduction in freight transportation costs offered by intermodal services. This cost advantage is driving businesses towards multimodal transportation, which combines two or more modes of transport, such as rail and trucking, to move goods efficiently and cost-effectively. However, the market faces substantial challenges. Infrastructure costs pose a significant hurdle, as the development and maintenance of intermodal terminals and railways require substantial investments. These expenses can deter potential entrants and limit the market's growth potential.
- To capitalize on the cost advantages of intermodal transportation while mitigating infrastructure challenges, companies must explore innovative financing models and collaborate with governments and industry partners to share infrastructure costs and optimize resource utilization. By addressing these challenges, businesses can effectively navigate the market and position themselves for long-term success.
What will be the Size of the Intermodal Freight Transportation Market during the forecast period?
Explore in-depth regional segment analysis with market size data - historical 2019-2023 and forecasts 2025-2029 - in the full report.
Request Free Sample
Intermodal freight transportation continues to evolve, with dynamic market trends shaping its landscape. Logistics management seeks to optimize carbon emission reduction through the adoption of fuel-efficient intermodal solutions, such as rail freight. The hub-and-spoke model facilitates the efficient movement of goods, with railways and ports serving as crucial infrastructure components. Container cleaning, cargo insurance, and container repair are essential services ensuring the integrity of intermodal containers. Double-stack railcars and last mile delivery solutions enhance capacity and efficiency, while road infrastructure and container handling equipment facilitate seamless intermodal transfers. Artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics are transforming intermodal operations, from route optimization and supply chain optimization to intermodal terminal management and container tracking systems.
Intermodal regulations and container security remain paramount, with ongoing advancements in container standardization and capacity management. The intermodal network encompasses a diverse range of container types, including flat racks, dry vans, reefers, tank containers, and open tops. Intermodal regulations, shipping schedules, and freight forwarding services ensure the smooth flow of goods. Road haulage and intermodal terminals are integral components of the intermodal network, with yard management systems and container chassis enabling efficient container movement. Environmental impact and container leasing are increasingly important considerations, with ongoing efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable intermodal practices.
Blockchain technology and crane operations further enhance intermodal operations, ensuring transparency and efficiency. Overall, the market remains a dynamic and evolving landscape, with ongoing advancements shaping its future.
How is this Intermodal Freight Transportation Industry segmented?
The intermodal freight transportation industry research report provides comprehensive data (region-wise segment analysis), with forecasts and estimates in "USD billion" for the period 2025-2029, as well as historical data from 2019-2023 for the following segments.
- Mode Of Transportation
- Rail transport
- Road transport
- Sea transport
- Product
- Minerals and ores
- Food and farm products
- Equipment and instruments
- Chemicals
- Others
- End-user Industry
- Manufacturing
- Oil and Gas
- Consumer and Retail
- Energy and Mining
- Others
- Manufacturing
- Oil and Gas
- Consumer and Retail
- Energy and Mining
- Others
- Geography
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- UK
- APAC
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Rest of World (ROW)
- North America
.
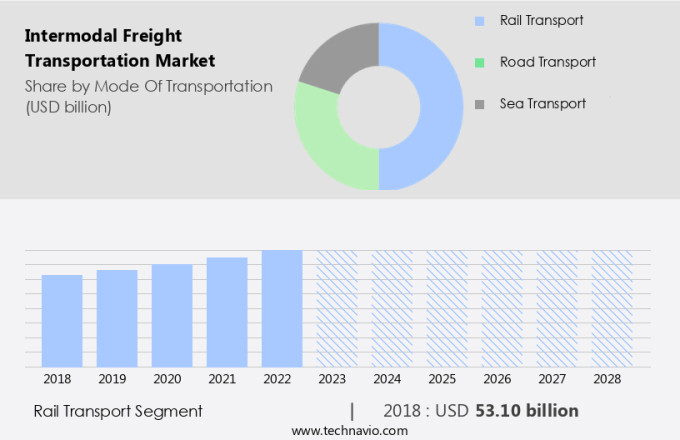
By Mode Of Transportation Insights
The rail transport segment is estimated to witness significant growth during the forecast period.
The Rail transport segment was valued at USD 56.00 billion in 2019 and showed a gradual increase during the forecast period.
Regional Analysis
North America is estimated to contribute 33% to the growth of the global market during the forecast period. Technavio's analysts have elaborately explained the regional trends and drivers that shape the market during the forecast period.
The market in North America is experiencing moderate growth due to the gradual expansion of the manufacturing and industrial sectors. This growth is driven in part by the increase in freight volumes at US ports of entry, as trade between North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) countries continues to grow. Major goods transported across the border include apparel, food, machinery, furniture, and electrical equipment. Intermodal freight transportation offers several advantages, including carbon emission reduction through improved fuel efficiency, logistical management, and the hub-and-spoke model. Rail freight plays a significant role in this market, with the use of double-stack railcars and intermodal terminals facilitating the efficient movement of goods.
Container security and regulations are essential considerations in this market, with the implementation of container tracking systems, container modification, and container cleaning ensuring the safe and secure transportation of cargo. Intermodal regulations also impact the market, with the need for compliance driving the adoption of yard management systems and container handling equipment. The integration of technology, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology, is transforming the market. This includes the optimization of routes, railway and port infrastructure, and supply chain processes. Container leasing and standardization, as well as capacity management and shipping schedules, are also key factors influencing market dynamics.
Last mile delivery and road haulage are crucial components of the intermodal freight transportation network, with road infrastructure and container chassis essential for the efficient movement of goods from the terminal to their final destination. Freight forwarding and data analytics are also important considerations, with the need for real-time information and efficient cargo insurance facilitating seamless transportation. Environmental impact is a growing concern in the market, with the adoption of eco-friendly practices, such as the use of reefer and tank containers, and the optimization of shipping schedules, helping to reduce carbon emissions. Overall, the market in North America is evolving to meet the changing needs of industry and consumers, with a focus on efficiency, sustainability, and innovation.
Market Dynamics
Our researchers analyzed the data with 2024 as the base year, along with the key drivers, trends, and challenges. A holistic analysis of drivers will help companies refine their marketing strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
What are the key market drivers leading to the rise in the adoption of Intermodal Freight Transportation Industry?
- Intermodal services, which reduce freight transportation costs, serve as a significant market driver by providing an efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional trucking methods.
- Intermodal freight transportation, which involves the use of multiple modes of transport, including flat rack containers, dry van containers, reefer containers, and tank containers, has gained popularity among shippers due to its cost advantages. This transportation method combines sea or river transportation for the bulk of the journey, followed by rail freight for long-distance transport, and finally, road transportation for the last mile delivery. The hub-and-spoke model of intermodal freight transportation further enhances its cost efficiency. The rising cost of road freight carriers has made intermodal freight transportation an attractive alternative. The cost of intermodal freight transportation can be broken down into fuel, labor, and equipment.
- Any fluctuations in the cost of these categories directly impact the bottom line of road freight carriers. In addition, intermodal freight transportation offers other benefits such as improved carbon emission reduction through increased fuel efficiency and enhanced container security. Intermodal regulations ensure the safety and security of goods during transportation, making it a preferred choice for logistics management. Overall, intermodal freight transportation offers a cost-effective, efficient, and secure solution for freight transportation.
What are the market trends shaping the Intermodal Freight Transportation Industry?
- The increasing preference for multimodal transportation represents a significant market trend. This transportation approach, which combines two or more modes of travel, is gaining widespread acceptance among consumers and industry professionals alike.
- Intermodal freight transportation involves the use of multiple modes of transport, including railway infrastructure and road infrastructure, to move containers from one place to another under separate contracts with various carriers. This contrasts with multimodal transportation, which is characterized by a single contract and a single transport carrier responsible for moving goods across all modes. The advantages of intermodal transportation include route optimization, reduction of cargo damage due to container cleaning and repair, and cargo insurance coverage. The use of double-stack railcars and container handling equipment at ports and railway stations streamlines the loading and unloading process.
- Furthermore, the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) and supply chain optimization techniques enhances the efficiency and productivity of intermodal transportation. Last mile delivery challenges are addressed through collaborative efforts between transportation providers and logistics companies. The growing emphasis on reducing road congestion and improving sustainability in the transportation sector is expected to fuel the demand for intermodal freight transportation.
What challenges does the Intermodal Freight Transportation Industry face during its growth?
- The escalating infrastructure costs represent a significant obstacle to the expansion and growth of the industry.
- Intermodal freight transportation involves the transfer of containers between different modes of transport, including air, rail, and road. The market relies heavily on infrastructure investments to facilitate seamless transfers. Gantry and heavy-duty cranes are essential for lifting and transferring ISO containers between ships and intermodal terminals. These cranes enable the efficient conversion of containers from open top to standard ISO containers during the transfer process. Moreover, container tracking systems and yard management systems play a significant role in capacity management. Container modification is another critical aspect of intermodal transportation, ensuring containers are suitable for various cargo types and transportation modes.
- Intermodal networks rely on container chassis for efficient movement between terminals and transportation modes. Investments in rail and road access are also vital for intermodal transportation. Seaports require rail lines to enable railway transport of goods, while roads facilitate the movement of trucks to and from terminals. By investing in these infrastructure components, intermodal transportation enhances logistical efficiency and supports global trade.
Exclusive Customer Landscape
The intermodal freight transportation market forecasting report includes the adoption lifecycle of the market, covering from the innovator's stage to the laggard's stage. It focuses on adoption rates in different regions based on penetration. Furthermore, the intermodal freight transportation market report also includes key purchase criteria and drivers of price sensitivity to help companies evaluate and develop their market growth analysis strategies.
Customer Landscape
Key Companies & Market Insights
Companies are implementing various strategies, such as strategic alliances, intermodal freight transportation market forecast, partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, geographical expansion, and product/service launches, to enhance their presence in the industry.
AP Moller Maersk AS - The company specializes in comprehensive intermodal freight transportation solutions, encompassing Ocean Transport, Inland Services, Cross Border Rail Transportation, Air Freight via Maersk, and Less than Container Load services.
The industry research and growth report includes detailed analyses of the competitive landscape of the market and information about key companies, including:
- AP Moller Maersk AS
- BDP International Inc.
- C H Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- Convoy Inc.
- CSX Corp.
- Deutsche Bahn AG
- Deutsche Post AG
- Elemica Inc.
- Hapag Lloyd AG
- J B Hunt Transport Services Inc.
- Koerber AG
- Kuehne Nagel Management AG
- Lynden Inc.
- MARTEN TRANSPORT LTD.
- Trimble Inc.
- Uber Technologies Inc.
- United Parcel Service Inc.
- Westinghouse Air Brake Technologies Corp.
- WiseTech Global Ltd.
- XPO Inc.
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of companies has been conducted to help clients understand the wider business environment as well as the strengths and weaknesses of key industry players. Data is qualitatively analyzed to categorize companies as pure play, category-focused, industry-focused, and diversified; it is quantitatively analyzed to categorize companies as dominant, leading, strong, tentative, and weak.
Recent Development and News in Intermodal Freight Transportation Market
- In February 2024, Maersk and DB Schenker, two leading players in the market, announced a strategic partnership to enhance their rail and road intermodal services. This collaboration aimed to create a more efficient and sustainable multimodal network, reducing the carbon footprint of their combined operations (Maersk press release, 2024).
- In May 2024, Cargotec Corporation, a key player in cargo handling solutions, launched the Kalmar Autonomous Rail Mounted Gantry (RMG) crane. This technological advancement marked the first fully autonomous RMG crane in intermodal terminals, promising increased productivity and efficiency (Cargotec press release, 2024).
Research Analyst Overview
- In the dynamic market, containerized cargo continues to dominate, driving the need for efficient freight consolidation and intermodal transfers. Delivery time is a critical factor, with third-party logistics (3PL) providers optimizing modal split to ensure seamless cross-border shipping. Container dimensions and weight play a significant role in cargo handling and intermodal connectivity, impacting lead time and customs clearance. Intermodal freight transportation involves interplay between container depots, shipping documentation, and bill of lading. Transit time is a crucial metric, with trade compliance and cargo manifest essential for efficient cargo handling. Container stacking and inspection are integral parts of container yard operations, requiring cost optimization and empty container management.
- Freight invoices and freight brokerage are essential components of international freight, with intermodal connectivity and transit time impacting container dwell time. Intermodal freight transportation requires careful coordination between container yard, customs clearance, and cargo handling to minimize costs and maintain integrated logistics. Container sealing and inspection ensure secure and compliant shipping, while intermodal transfers and intermodal connectivity streamline the transportation process. Domestic freight and international freight each present unique challenges, requiring effective management of containerized cargo, delivery time, and transit time.
Dive into Technavio's robust research methodology, blending expert interviews, extensive data synthesis, and validated models for unparalleled Intermodal Freight Transportation Market insights. See full methodology.
|
Market Scope |
|
|
Report Coverage |
Details |
|
Page number |
212 |
|
Base year |
2024 |
|
Historic period |
2019-2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2025-2029 |
|
Growth momentum & CAGR |
Accelerate at a CAGR of 7.2% |
|
Market growth 2025-2029 |
USD 69.4 billion |
|
Market structure |
Fragmented |
|
YoY growth 2024-2025(%) |
6.6 |
|
Key countries |
US, China, Canada, Germany, UK, India, France, Italy, Japan, and South Korea |
|
Competitive landscape |
Leading Companies, Market Positioning of Companies, Competitive Strategies, and Industry Risks |
What are the Key Data Covered in this Intermodal Freight Transportation Market Research and Growth Report?
- CAGR of the Intermodal Freight Transportation industry during the forecast period
- Detailed information on factors that will drive the growth and forecasting between 2025 and 2029
- Precise estimation of the size of the market and its contribution of the industry in focus to the parent market
- Accurate predictions about upcoming growth and trends and changes in consumer behaviour
- Growth of the market across North America, Europe, APAC, Middle East and Africa, and South America
- Thorough analysis of the market's competitive landscape and detailed information about companies
- Comprehensive analysis of factors that will challenge the intermodal freight transportation market growth of industry companies
We can help! Our analysts can customize this intermodal freight transportation market research report to meet your requirements.